⬤ A Morgan Stanley survey has uncovered strong momentum in humanoid robotics adoption across Chinese enterprises. The data shows 62 percent of companies are positioning themselves as likely adopters, planning to roll out wheel-based or leg-based humanoid robots within the next three years. This trend points to growing corporate appetite for robotics as automation becomes a strategic priority.
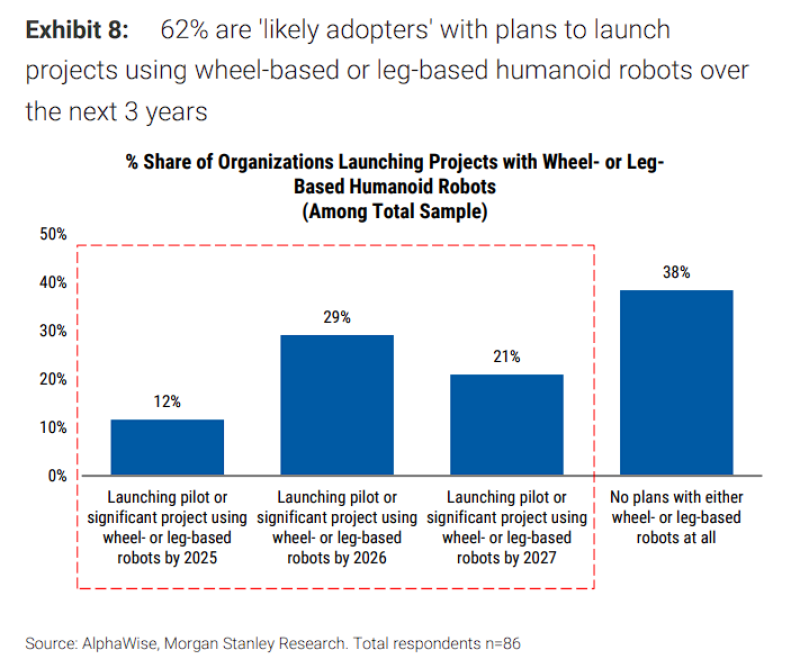
⬤ The adoption timeline shows clear acceleration: 12 percent of organizations expect to kick off major humanoid robot projects by 2025, jumping to 29 percent in 2026 and 21 percent in 2027. Just 38 percent have no deployment plans on the horizon. When it comes to vendor preferences, Unitree stands out with 60 percent of likely adopters actively evaluating its systems. DeepRobotics follows at 28 percent, with UBTECH close behind at 27 percent. Midea captures 17 percent interest, EngineAI sits at 13 percent, while smaller groups are looking at Tian Gong, Xiaomi, Dobot and other players. Western developers show lower engagement—Figure registers at 4 percent and XPENG at 2 percent.
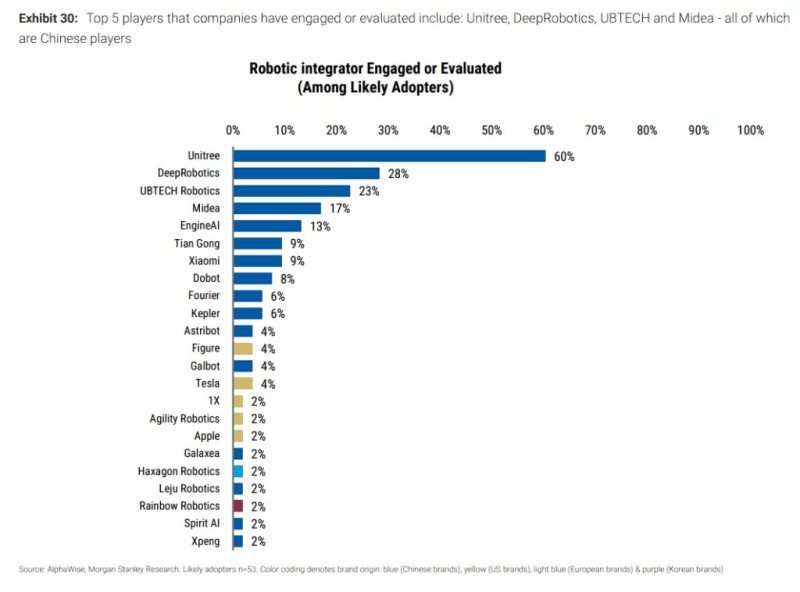
⬤ The numbers reflect a fundamental shift toward automation as companies explore humanoid robots for logistics, assembly, and facility management tasks. Chinese robotics firms currently lead early evaluation stages thanks to competitive pricing, fast innovation cycles, and a robust domestic ecosystem. Still, interest in global platforms signals intensifying competition around robotics hardware, autonomy software, and integration solutions.

⬤ These trends carry real weight for labor strategies, capital spending, and long-term automation roadmaps. With most surveyed companies eyeing humanoid systems, the robotics sector looks set for rapid commercial growth—potentially reshaping productivity benchmarks and investment priorities across industries.
 Eseandre Mordi
Eseandre Mordi

 Eseandre Mordi
Eseandre Mordi


