⬤ The AI landscape just got a fresh contender. Memento, a newly released open-source framework, is making waves by letting LLM agents get smarter over time without touching their core model weights. Instead of going through the usual fine-tuning grind, the system learns from experience by storing and pulling up structured cases when needed. This memory-driven approach marks a real departure from how most AI training works today, and the research paper backing it up shows some pretty solid numbers across challenging benchmarks.
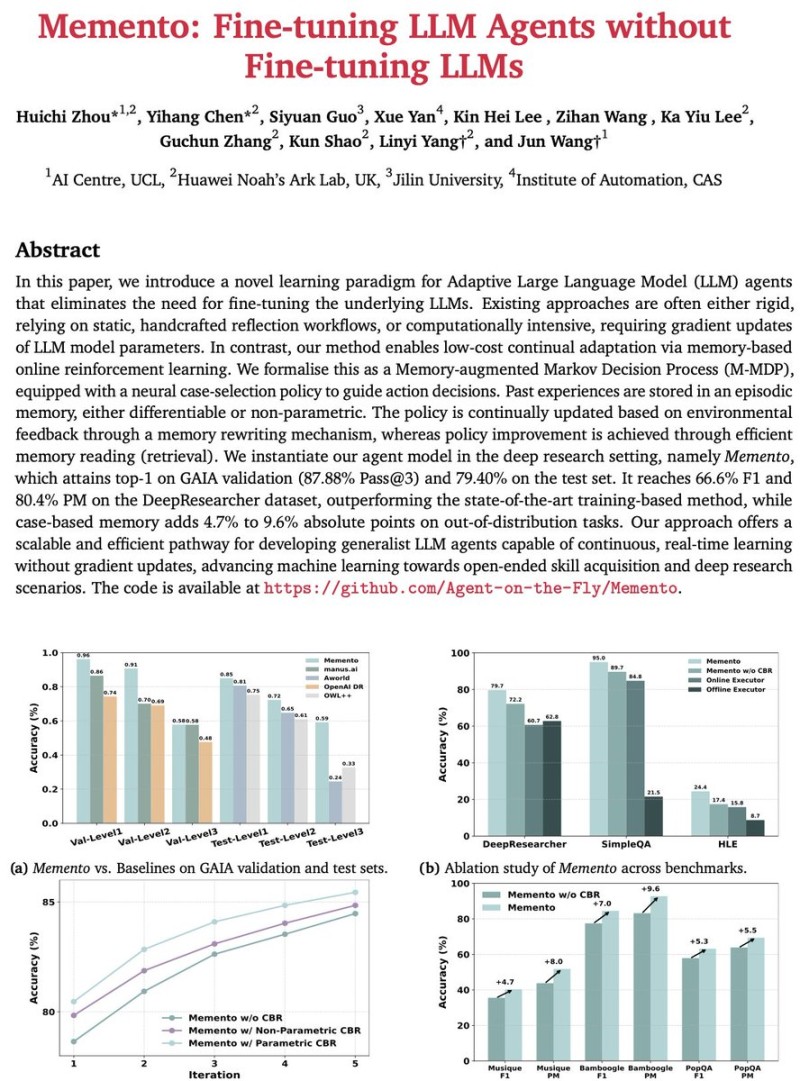
⬤ Here's how it works: Memento builds a case-based memory bank that tracks everything—previous tasks, the steps taken, which tools were used, and what happened in the end. When a new task comes in, the agent digs through similar past cases to plan and execute more efficiently. The system splits responsibilities between a planner and an executor. The planner breaks down tasks, finds relevant examples from memory, and maps out a strategy. The executor handles the actual work—running searches, executing code, processing documents through the Model Context Protocol. Performance-wise, Memento hit 87.88% Pass@3 on GAIA validation and 79.40% on the test set, beating several established systems. On trickier out-of-distribution tasks, it showed improvements of up to 9.6 percentage points.
⬤ The numbers across other benchmarks tell a similar story. Memento pulled ahead on DeepResearcher, SimpleQA, and HLE tests, consistently outperforming competing baselines. The ablation studies—where researchers test what happens when you remove certain features—showed that case-based reasoning alone added between 4.7 and 9.6 percentage points to accuracy. That's significant. It confirms that memory retrieval isn't just a nice add-on; it's central to handling complex, multi-step tasks. And unlike resource-heavy fine-tuning methods, Memento keeps improving without burning through massive compute budgets.

⬤ Why does this matter? Because Memento offers a practical way to build AI agents that actually get better through real-world use. No weight updates, no expensive retraining cycles—just continuous learning from what's already happened. That could reshape how companies think about AI infrastructure, efficiency, and staying competitive in machine learning. Plus, it's open-source, which means teams exploring sustainable, high-performance AI systems now have a serious new tool to work with.
 Saad Ullah
Saad Ullah

 Saad Ullah
Saad Ullah


