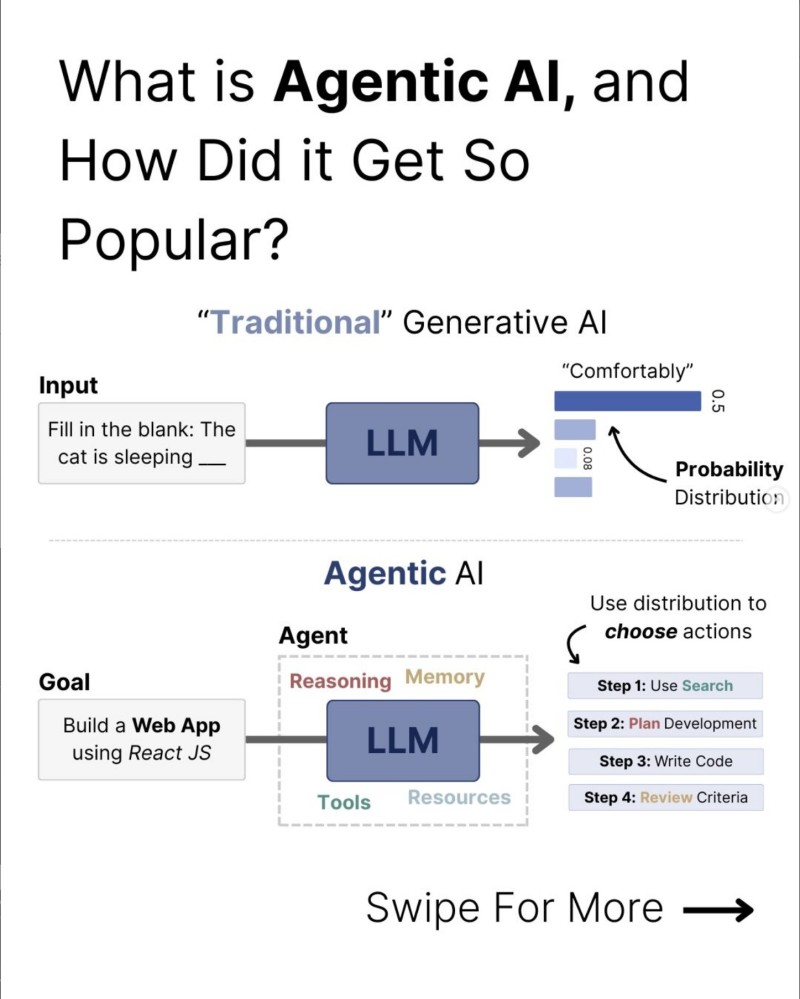
⬤ Agentic AI is picking up serious momentum as companies roll out autonomous systems that handle complex, multi-step tasks without human involvement. These systems use specialized LLM agents that plan ahead, make decisions, and tap into external tools—a major leap from traditional generative AI that just spits out text responses. Visual breakdowns show how Agentic AI turns simple prompts into structured workflows powered by autonomous decision-making cycles.
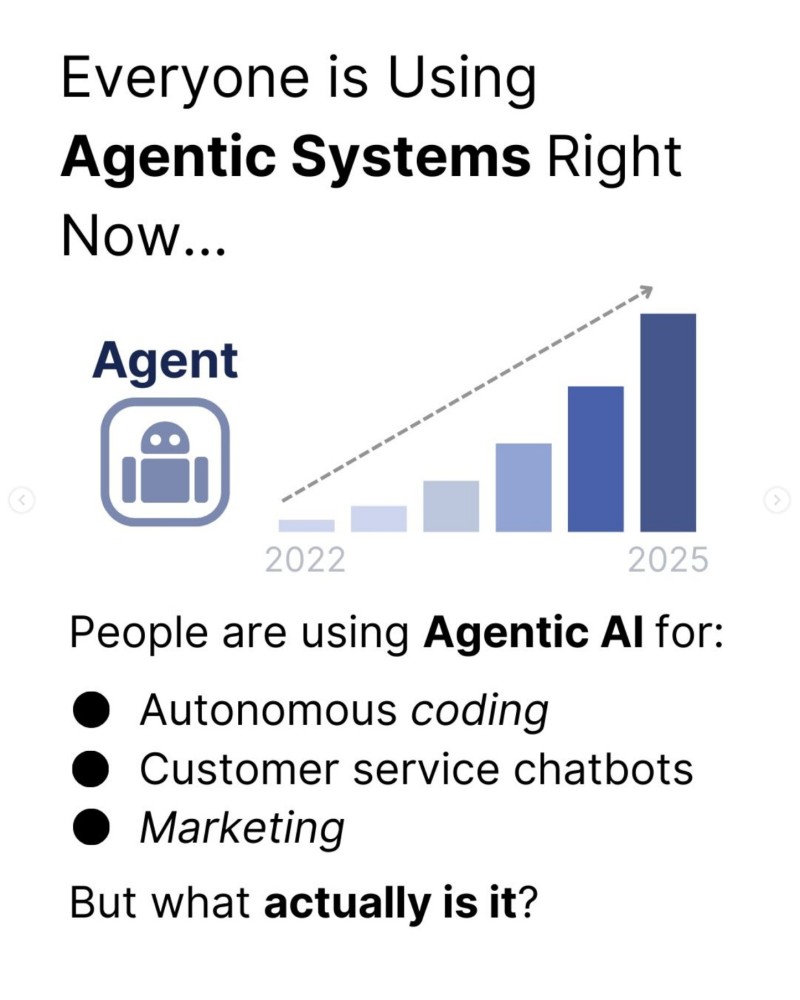
⬤ These AI systems work through smaller, focused agents that gather information, reason through goals, take action with integrated tools, and learn from results. Real applications include autonomous coding, automated customer service, marketing workflows, and financial analysis. An agent can research someone, draft an email, check a calendar through an API, and send the message—all from one user prompt, as long as it has the right permissions.
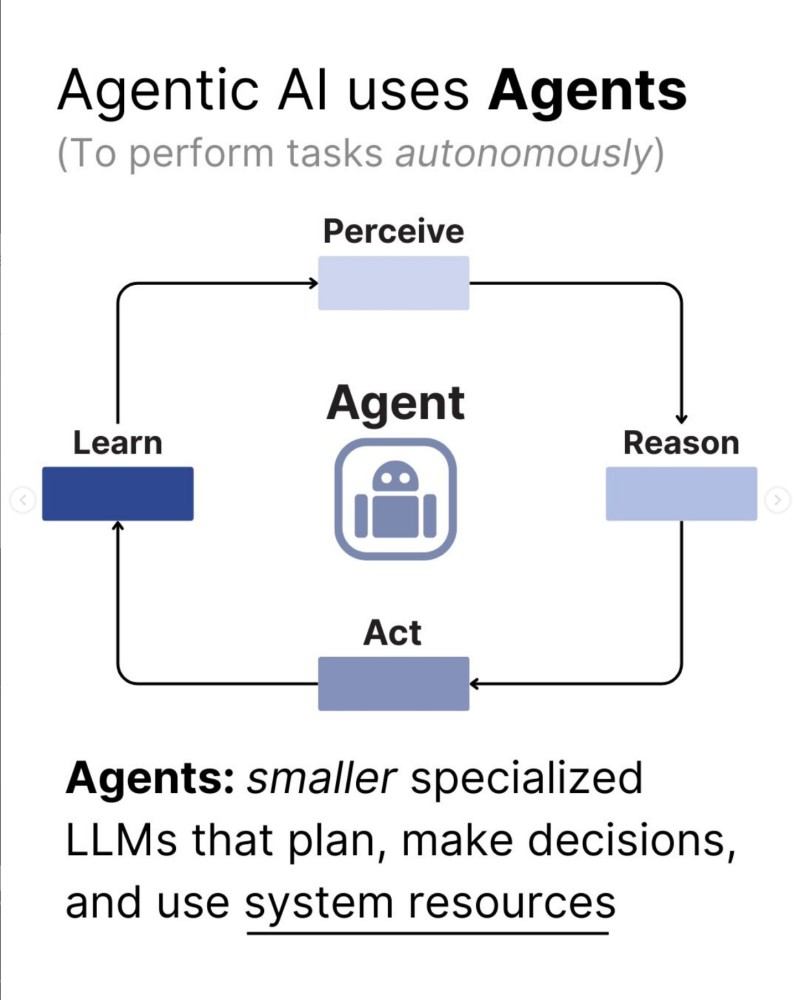
⬤ The core of Agentic AI runs on a four-step loop. First, agents perceive their environment by pulling data from APIs, databases, and digital sources. They reason using techniques like Chain-of-Thought or Monte Carlo Tree Search, breaking big goals into doable subtasks. Next, they act—writing code, calling tools, or connecting with external systems.
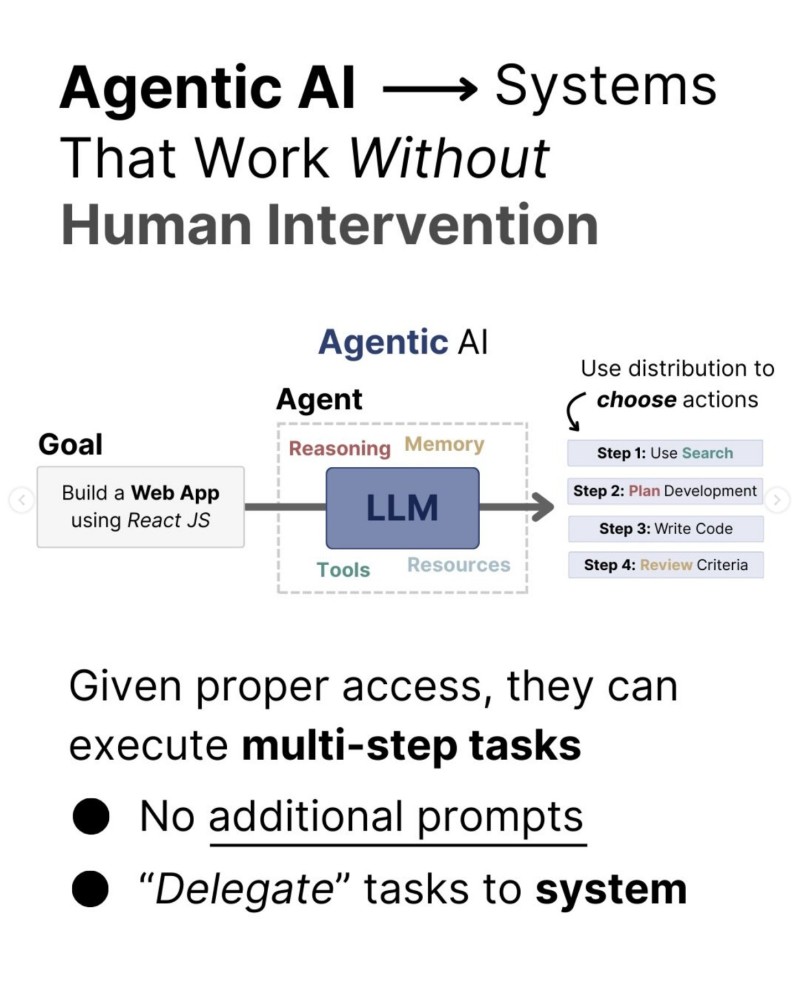
⬤ The learning phase completes the cycle as agents compare outcomes against objectives and update their internal state. Structured memory systems—working, episodic, and semantic—help maintain context across long tasks. This memory architecture allows agents to handle extended workflows while keeping track of past actions and decisions.
⬤ The surge in Agentic AI adoption signals a major shift toward automation-driven intelligence. Organizations are betting on scalable, autonomous decision-making systems that deliver efficiency gains and unlock new workflow capabilities. As these models embed deeper into operations, Agentic AI looks set to play a defining role in the next wave of digital transformation across industries.
 Sergey Diakov
Sergey Diakov

 Sergey Diakov
Sergey Diakov


