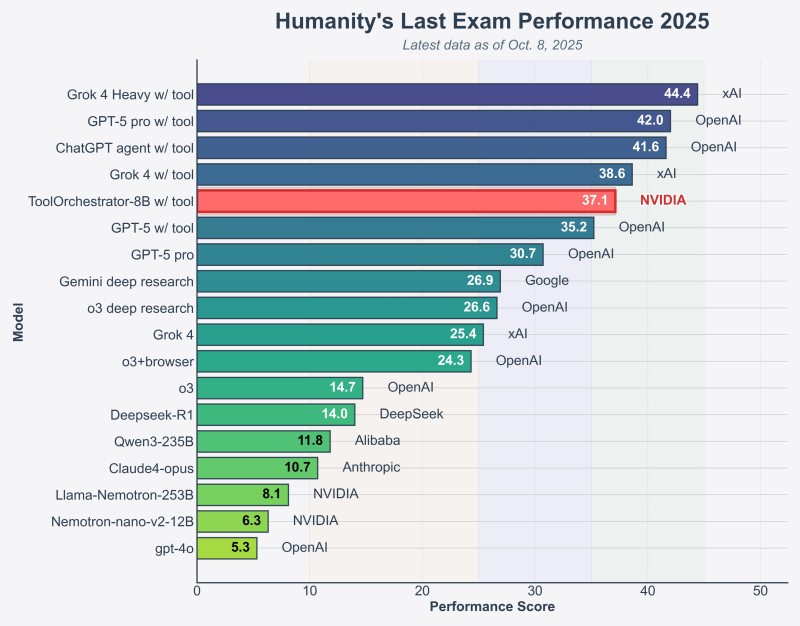
⬤ NVIDIA caught the market's eye after benchmark results showed its ToolOrchestrator-8B pulling ahead in agent-orchestration tech. The model scored 37.1% on Humanity's Last Exam, edging past GPT-5's 35.1% while being roughly 2.5× more efficient. Visual data confirms Orchestrator-8B ranks among the top-performing models released so far, sitting above multiple tool-augmented systems from rival AI labs.
⬤ Orchestrator-8B functions as a router model that decides whether to answer prompts directly or call external tools like search engines, code interpreters, APIs, or other LLMs. It's trained on ToolScale, a massive synthetic dataset built to teach agents how to route tasks based on price, speed, and quality trade-offs. Each training example includes a user query, available tools with their costs, a sequence of tool calls, and a final answer—helping the model learn realistic, budget-conscious decision-making.
⬤ ToolScale itself gets generated by another LLM that builds domain-specific databases, constructs tool APIs, and creates multi-step tasks with ground-truth tool traces. This setup allows Orchestrator-8B to learn accurate, speed-sensitive, cost-balanced routing instead of defaulting to the priciest model every time. Across benchmarks including HLE, FRAMES, and tau-squared, the Qwen3-8B-based orchestrator reportedly beat tool-augmented GPT-5, Claude Opus 4.1, and Qwen3-235B-A22B while skipping unnecessary high-cost compute calls. Benchmark charts back this up, showing Orchestrator-8B ranked above GPT-5 w/tool at 35.2%, GPT-5 pro at 30.7%, Gemini Deep Research at 26.9%, and other leading models.
⬤ Orchestrator-8B's performance signals a broader industry pivot toward small, efficient routing models that coordinate tools rather than relying on ever-larger monolithic LLMs. For the AI sector, this result shows how cost-aware agent systems might reshape compute demand, API pricing, and the evolution of multi-model orchestration frameworks going forward.
 Sergey Diakov
Sergey Diakov

 Sergey Diakov
Sergey Diakov


