⬤ Recent forecasts point to a fundamental shift in global AI compute demand. Training workloads are set to peak next year before beginning a sustained decline. Research data reveals that AI inference operations will accelerate sharply throughout the decade, eventually becoming the primary driver of compute consumption. This transition matters significantly for semiconductor companies like NVDA, whose data center revenues have been fueled largely by training-intensive workloads.
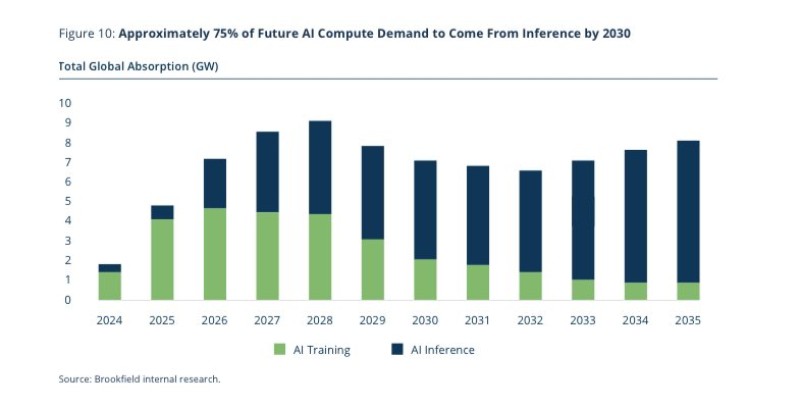
⬤ The data shows global compute absorption climbing through 2028 before stabilizing, though the mix of workloads changes dramatically. Training dominates in 2024 and 2025, but by 2030, inference represents roughly 75% of total demand. By 2035, inference consumption exceeds 8 GW while training drops below 2 GW. This growing gap stems from the expected surge in real-time AI applications that need constant, large-scale inference rather than occasional high-intensity training cycles. Such a shift would favor chips designed for inference efficiency over the training-focused designs that have traditionally benefited NVDA.

⬤ The projections also highlight substantial growth in specialized silicon. Custom ASICs are estimated to comprise 25% of the installed chip base by 2035. This suggests purpose-built inference processors could increasingly capture market share from NVDA as hyperscalers and businesses pursue better efficiency and lower costs. The evolving landscape presents what some view as a significant long-term challenge, particularly if the pivot toward inference-heavy workloads reshapes competitive dynamics in AI hardware.
⬤ The expected shift from training-focused to inference-dominated markets carries major implications for the semiconductor industry. As AI deployments scale and real-time model execution becomes the main computational need, efficiency-optimized architectures and custom accelerators may assume larger roles in infrastructure planning. The changing workload composition, paired with rising ASIC adoption, highlights how shifting AI demand patterns could redefine strategic priorities across the sector.
 Usman Salis
Usman Salis

 Usman Salis
Usman Salis


