⬤ Recent research from the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory reveals that how you write your prompts can dramatically reduce hallucinations in ChatGPT and similar AI tools. The team tested various prompting approaches across 1,200 queries and found that strategic phrasing techniques cut false responses by more than 20 percentage points compared to standard prompting methods.
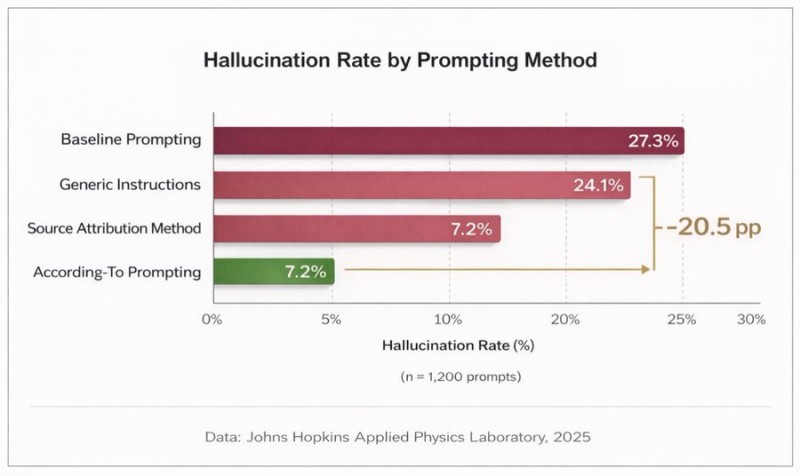
⬤ The numbers tell a compelling story. Basic prompting produced hallucinations 27.3% of the time, while adding generic instructions only improved things slightly to 24.1%. But when researchers used the Source Attribution Method, asking the AI to cite verifiable sources, the hallucination rate plummeted to just 7.2%. The "According-To Prompting" technique, which requires AI responses to explicitly reference checkable information rather than generate narrative answers, matched that 7.2% rate.
⬤ The research comes at a crucial time, following high-profile cases where people trusted fabricated AI outputs with serious consequences. One notable incident involved a lawyer who faced professional repercussions after submitting AI-generated legal citations that turned out to be completely fake. These findings suggest that users have more control over AI accuracy than previously thought.
⬤ For businesses and professionals in fields like finance, law, and medicine, this research offers practical solutions. Instead of waiting for better AI models or investing in expensive infrastructure upgrades, organizations can improve reliability right now by teaching teams better prompting techniques. That said, the study reinforces that human verification remains essential, no matter how good the prompting gets.
 Artem Voloskovets
Artem Voloskovets

 Artem Voloskovets
Artem Voloskovets


