⬤ Google released two systems called Titans besides MIRAS. MIRAS is a memory framework that lets an AI model keep information and update it during a chat instead of forgetting everything after each exchange. It combines the speed of older RNN systems with the strength of Transformers - it can work through very long passages without being overwhelmed.
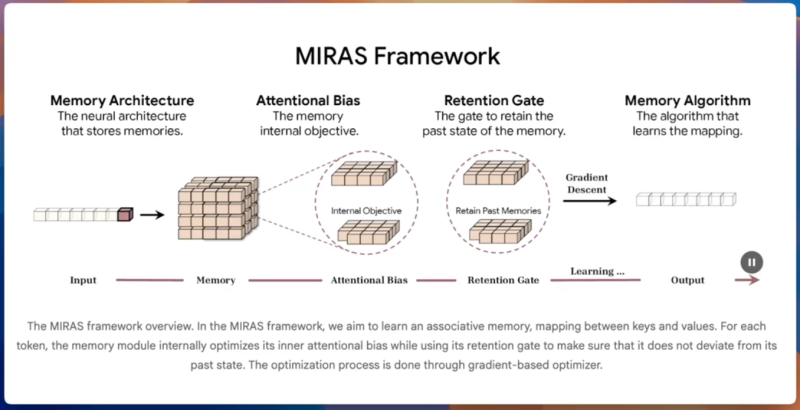
⬤ MIRAS contains a neural memory module that changes when new data arrive. An attention unit and a retention gate judge which parts of earlier input deserve to stay. Google reports that the system copes with contexts beyond two million tokens, far above the usual Transformer limit. Rather than simply widening the window, MIRAS stores items that a “surprise” signal marks as novel or important.
Google states: MIRAS refines its internal memory through gradient based optimization enabling stable learning without deviating from past states.
⬤ The framework trains itself through gradient based optimization - it learns while preserving what it already knows. Titans is shipped together with MIRAS as part of a wider plan to build models that reason, remember plus adapt over long periods. The approach favors smarter architecture over raw hardware increases.

⬤ For the AI field, MIRAS is significant because it alters structure, not only benchmark scores. Models that possess genuine memory could reshape enterprise AI, let chatbots improve across sessions and guide the design of later systems. As competition toward AGI intensifies, such frameworks may define how AI stores knowledge and performs complex reasoning at scale.
 Peter Smith
Peter Smith

 Peter Smith
Peter Smith


