⬤ Pixeltable's open-source framework is catching developers' attention as the industry rethinks how AI systems actually work. The reality? Up to 95 percent of AI engineering today revolves around context engineering, not model size. Even the most powerful model falls flat if the information feeding it is messy or incomplete. The framework breaks down six key components: prompting techniques, query augmentation, memory systems, retrieval pipelines, agents, and tools.
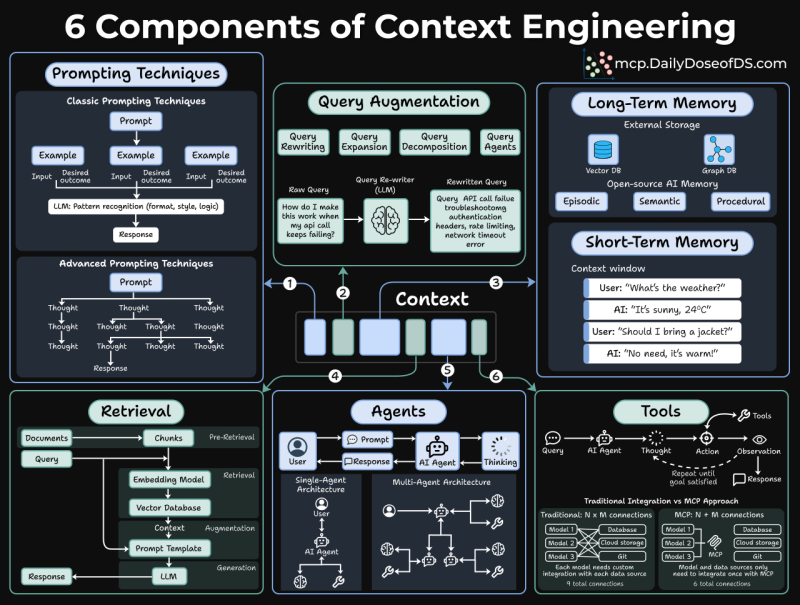
⬤ Strong AI performance demands more than just throwing a big model at the problem. Short-term memory keeps conversations flowing, long-term memory stores user preferences and history, while retrieval components pull the right documents at the right time. Most developers end up building and connecting five separate systems just to keep things running smoothly. Pixeltable's pitch is simple: unify everything. Documents, embeddings, conversation history, and agent outputs all live as tables in one place. Embeddings update automatically as computed columns, and vector search works right alongside regular data operations.
⬤ The unified setup brings real benefits: retrieval-augmented generation without juggling multiple databases, long-term memory powered by vector search across old conversations, and multi-agent workflows that save automatically. The framework isn't trying to replace language models—it's cutting out the integration headaches that slow teams down when they're coordinating APIs, databases, and agent frameworks.
⬤ As AI spreads across industries, unified context systems could reshape how teams build data pipelines, allocate resources, and design long-term infrastructure. The framework shows that retrieval, memory, and agent orchestration are becoming the real drivers of AI reliability and efficiency. With open-source tools gaining momentum, context engineering may define how enterprise AI systems scale in the years ahead.
 Marina Lyubimova
Marina Lyubimova
 Marina Lyubimova
Marina Lyubimova


