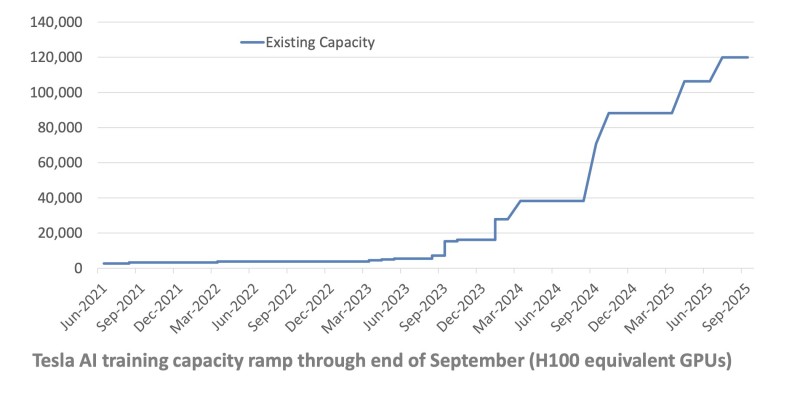
Tesla's AI training infrastructure has hit a massive milestone — 120,000 GPUs now power the company's Full Self-Driving system. A shared chart clearly shows Tesla's exponential growth in computing capacity, measured in H100-equivalent GPUs, from mid-2023 through September 2025.
At the start of 2023, Tesla's compute power remained relatively flat. Then, beginning in early 2024, the line shows sharp increases — from roughly 40,000 to over 80,000 GPUs, and then to the current 120,000 units by late 2025. This reflects one of the most aggressive AI scaling curves in the industry, placing Tesla among the few global players competing at hyperscale levels alongside NVIDIA, Google, and OpenAI.
Why This Expansion Matters for FSD and Dojo
According to trader Whole Mars Catalog, Tesla's compute acceleration isn't only about size — it's about speed and data efficiency. Every GPU added strengthens the company's ability to process vast streams of real-world driving data and train neural networks that power its Full Self-Driving software.
This scaling supports Tesla's in-house Dojo supercomputer, which was built to reduce reliance on NVIDIA's chips and optimize training for massive video datasets. The term "H100-equivalent" suggests that Tesla's own hardware and architecture — possibly custom Dojo nodes — now reach performance on par with NVIDIA's most advanced AI GPUs.
By combining Dojo's specialized chips with high-throughput clusters, Tesla can retrain and update its autonomy models faster, improving vehicle safety, accuracy, and real-time responsiveness.
Tesla's Growing Role in the AI Compute Race
As Big Tech companies race to dominate AI infrastructure, Tesla's rapid GPU expansion underscores its evolution from an automaker into a full-scale AI company. The firm's unique advantage lies in its real-world data — millions of hours of driving footage used to train perception and decision-making systems that no text-based AI lab can replicate.
With this compute growth, Tesla is closing the gap with leading AI labs not only in raw capacity but also in specialized model training for robotics and autonomy. This positions Tesla as a major contender in both AI infrastructure and applied intelligence — areas once thought to belong exclusively to tech giants like Google and Microsoft.
 Usman Salis
Usman Salis

 Usman Salis
Usman Salis


