⬤ Google DeepMind just rolled out Gemma Scope 2, a fresh interpretability toolkit built for the entire Gemma 3 model lineup. The release puts sparse autoencoders and transcoders into every single layer of every Gemma 3 model—from the smallest 270 million parameter version all the way up to the massive 27 billion parameter builds, covering both base and chat versions. It's basically giving researchers X-ray vision into how these models actually work under the hood.
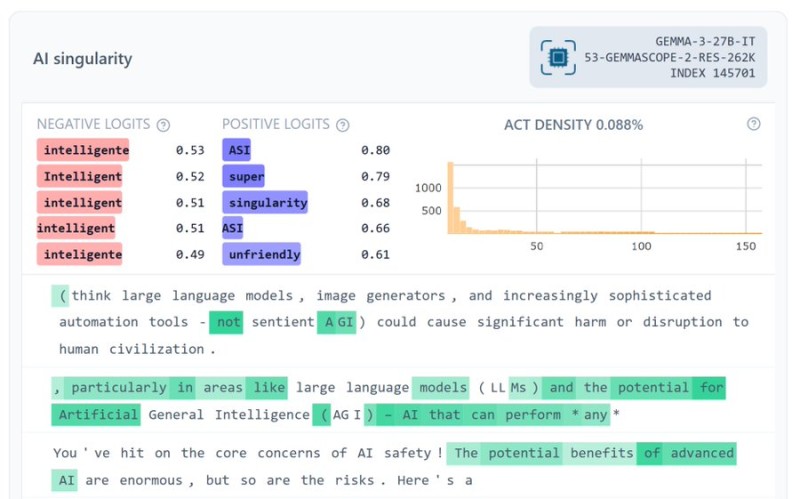
⬤ The toolkit lets you peek inside the model's brain while it's thinking. You can watch activations light up, see which concepts get stronger or weaker, and track how ideas bounce between layers as the model processes information. Instead of just looking at what comes out the other end, researchers can now see the whole journey—how specific thoughts form, shift, and eventually turn into responses.
⬤ "The goal of Gemma Scope 2 is to enable more ambitious open-source safety and interpretability research," according to Google DeepMind's announcement. The sparse autoencoders help pinpoint what's actually meaningful in all that neural noise, while the transcoders show how those signals morph as they move through the network. Together, they're designed to help researchers trace reasoning chains, spot potential problems, and finally understand what's really happening inside these black boxes.
⬤ This matters because AI interpretability is quickly becoming just as important as raw performance. By putting Gemma Scope 2 out there for anyone to use, Google DeepMind is giving the entire research community better tools to dissect, test, and audit how language models actually operate. It's a step toward making AI more transparent and accountable—something that'll shape how we build and deploy these systems going forward.
 Usman Salis
Usman Salis

 Usman Salis
Usman Salis


