OpenAI just made a significant move in AI safety with GPT-OSS-Safeguard—a new open-weight reasoning framework that puts policy-based decision-making right into the model's core. Now available in 120B and 20B parameter versions, it lets developers use their own written policies on the fly, moving away from rigid moderation systems toward something more adaptive and transparent.
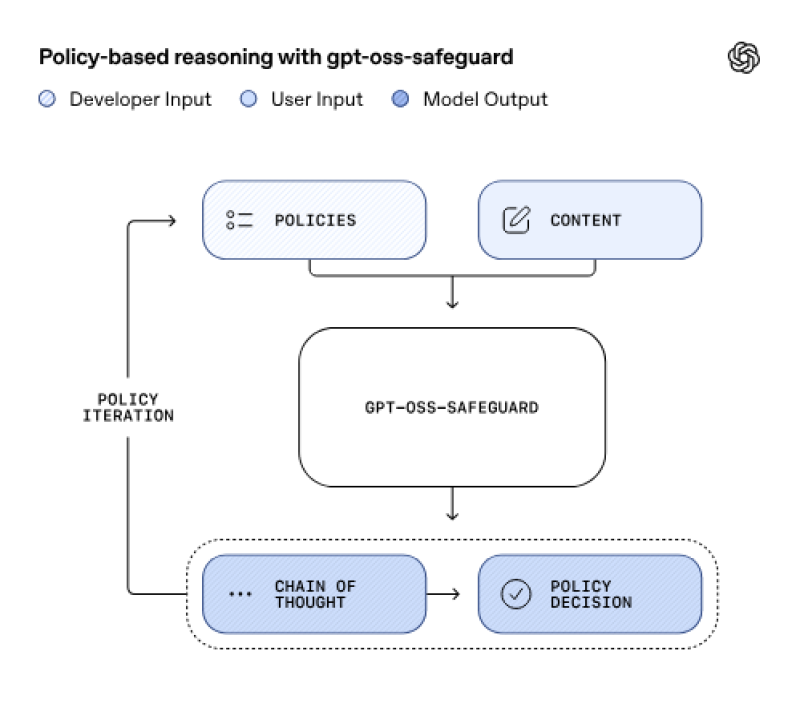
The OpenAI diagram shows exactly how it works: developer policies and user content go into the model, which then thinks through the decision using a chain of thought process. This creates what they call "policy iteration"—basically a feedback loop that keeps refining and explaining safety decisions in real time.
A Reasoning-First Approach to AI Safety
OpenAI describes GPT-OSS-Safeguard as a "reasoning-first safety tool," and that's exactly what sets it apart. Trader and AI analyst Ashutosh Shrivastava notes that instead of relying on baked-in moderation rules, the model takes whatever policy you give it at runtime and evaluates content based on that. Even better, it shows you its reasoning—explaining why it made each call.
This means you don't have to retrain classifiers every time your policies change. Just update your guidelines, and the model adapts. It's essentially a bring-your-own-policy system built for environments where risks and ethical standards keep evolving.
How It Actually Works
OpenAI's diagram breaks down the workflow into four key parts: policies (your safety guidelines), content (what needs to be analyzed), the GPT-OSS-Safeguard engine itself, and finally the chain of thought that leads to a policy decision.
The whole system is designed for iteration—you can review the reasoning, tweak your policies, and gradually improve both consistency and transparency.
Where This Really Shines
GPT-OSS-Safeguard works best in situations where traditional classifiers struggle: emerging risks where there's not much training data yet, highly nuanced content like legal or medical documents, and regulatory environments that change frequently. By making the reasoning visible, it opens the door to truly auditable AI moderation. You're not just seeing what the model decided—you're seeing how it got there.
The Tradeoffs
Of course, there's a catch. OpenAI admits this approach needs more computing power and takes longer than conventional classifiers. For massive, repetitive tasks with tons of labeled data, traditional models might still be the better choice. But when stakes are high and you need to understand the reasoning, that extra cost is worth it.
Open Access for Everyone
Both model versions are available on Hugging Face under the Apache 2.0 license, meaning researchers and companies can download, modify, and deploy them freely. The permissive licensing shows OpenAI's growing commitment to open safety research and collaborative governance.
 Eseandre Mordi
Eseandre Mordi

 Eseandre Mordi
Eseandre Mordi


