⬤ Sentient has launched ROMA, an open-source meta-agent framework that helps developers build scalable multi-agent AI systems using a recursive task execution model. ROMA breaks down complex tasks into structured subtasks that cooperating AI agents can handle, then merges the results into a single unified output. The framework aims to simplify workflow design, coordination, and traceability in advanced AI agent systems.
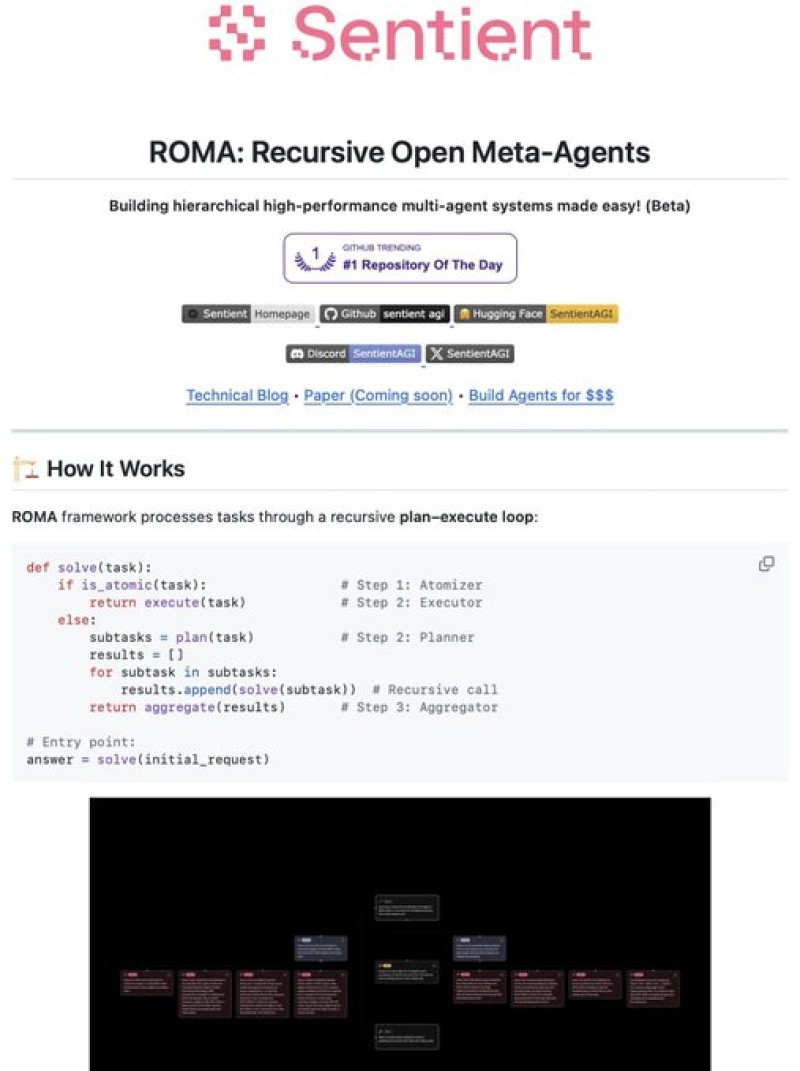
⬤ ROMA works through four core components that handle different parts of the task execution process. The Atomizer decides whether a task is simple enough to execute right away. The Planner breaks complex tasks into smaller, manageable pieces. The Executor carries out atomic tasks using LLMs, APIs, or other agents. Finally, the Aggregator compiles all the results back together. The framework follows a recursive loop—solve, decompose, execute, aggregate—allowing tasks to flow through a hierarchy while keeping everything organized. The entire project is open source and available on GitHub.
⬤ One of ROMA's standout features is its focus on transparency and workflow tracing. Developers can see exactly how tasks split into subtasks, watch how those subtasks get processed, and track how results come back together. This visibility makes complex AI systems easier to scale and debug, especially when you need multiple agents working together on layered objectives.

⬤ ROMA's release matters because multi-agent AI frameworks are becoming essential for building automated research tools, data-driven applications, and advanced digital assistants. By standardizing how tasks are broken down and coordinated, ROMA could speed up adoption of large-scale AI systems across different development environments while giving developers better clarity, control, and execution structure.
 Saad Ullah
Saad Ullah
 Saad Ullah
Saad Ullah


